Publisher
mattiny
Yamms - Yet another MultiMesh Scatter 3D
Yet another multi mesh scatter. A simple MultiMesh plugin where you can place your meshes into your scene via a configurable polygon area.
This plugin has been mirrored from the Godot Asset Library.
The plugin author is in no way affiliated with Gadget.
If you are the author of this plugin and would like this mirror removed, please contact support@gadgetgodot.com.
YAMMS - Yet Another MultiMesh Scatter
Table of Contents
- What is it?
- Features
- Installation
- Usage
What is it?
Yamms (Yet another multimesh scatter) is a plugin for Godot to place MultiMesh meshes into the game world.
Author: Mattiny
Youtube: https://youtu.be/2B_2qKIVYSs
- This plugin is only compatible with Godot 4.3 and following Godot versions.
- Version 1.2.0 of this plugin is NOT backwards compatible to previous plugin version.
Features
- Place MultiMeshInstances of different types into your scene.
- Configure the proportions (percentage) of how many meshes of each type shall be placed into your scene.
- Set up an area via Path3D polygon in which the meshes shall placed.
- Set up exclusion areas via Path3D polygons (inside your area definition) to leave these areas empty (for some or all items).
- Set up different placement algorythms for the MultiMeshInstances.
- Add additional scenes (e.g. collision objects) at the same position as the MultiMeshInstance3D instances.
Installation
- Download from GitHub: https://github.com/Mattiny/yamms
- Download via Asset library in Godot and activate the plugin.
Usage
MultiScatter
The MultiScatter is the main node of the whole MultiMesh scatter set up.
- In your Scene: Add the node "MultiScatter"
- Whenever the MultiScatter node is selected: The Editor shows buttons to set up a polygon. Add at least 3 point which span an area which is large enough to hold the meshes. Best practice: Change to orthogonal top view of your scene (key "7").
- In Inspector set up properties:
- Debug messages: Write additional output messages when generating the MultiMeshInstance3D positions. (as the name says: for debug purposes, when something does not work as expected)
- Amount: the amount of meshes which are generated into the scene.
- Seed: The random number generator seed. Using a seed makes the pattern of randomly generated meshes reproducible. Change the seed until you are satisfied with the result.
To prevent miscalculations of MultiMesh instance's position: Rotation of the MultiScatter object is not recommended. Therefore rotation is deactivated in the editor.
MultiScatterItem
The MultiScatterItem keeps information about one type of meshes in the MultiMesh set up. It needs to be a child node underneath the MultiScatter node. There can be multiple MultiScatterItems in one MultiScatter.
To prevent miscalculations of MultiMesh instance's position: Rotation of the MultiScatterItem object is not recommended. Therefore rotation is deactivated in the editor.
- In your scene: Add the node "MultiScatterItem" as a child node to a MultiScatter node.
- Select the MultiScatterItem.
Set up a MultiMeshInstance3D
- In the inspector: Paramter "MultiMesh": Create a new MultiMesh
- Click at the new MultiMesh: The MultiMesh parameters open and are editable
- set "Transform Format" to "3D"
- Drag & Drop a mesh from your file system into the inspector property "Mesh"
- If necessary: Drag & Drop a material for this mesh to inspector property "Geometry / Material override"
Set up parameters
- Percentage: The percentage proportion for this mesh. The exact amount depends on the "Amount" property of the parent MultiScatter and the proportion of sibling MultiScatterItems.
- Additional Scene: Places an additional scene (PackedScene) at the same position as the scattered item. Can be used e.g. to put collision objects at the same position. Note: It is a real scene, not a primitive MultiScatterItem3D. So it uses more resources at runtime than MultiMeshInstances. It is not supposed to be used with too many instances.
- Target Node: References the node where the scenes are placed in the scene tree. Note Don't place any other relevant Nodes of your scene underneath the referenced node. Whenever the MultiMeshInstance3D positions are generated, the target node will be deleted (without question).
- Additional scene: Reference to a PackedScene which will be instantiated and placed at the same position as the MultiMeshInstance3D.
PlacementMode
The PlacementMode sets up the algorythm to generate the position of the MultiMeshInstances. Add a placement mode as child element to the MultiScatterItem to set up and configure the algorythm. Some placement modes can contain a density map which can be adjusted by scaling, rotating and positioning the PlacementMode in the 3D scene. Because the placement mode algorythm is based on the plane it is only recommended to rotate the placement mode around the y-axis. Rotation around any other axis is not recommended. Therefore rotation around the x- and z-axis has been disabled in the editor.
Keep in mind the class "PlacementMode" is an abstract class and cannot be instantiated directly. Do not attach the "PlacementMode" itself to the MultiScatterItem. Instead add the specific placement mode. The following placement modes are available:
PMFlat
PMFlat - PlacementMode Flat - distributes the MultiMeshInstances on a flat plane. The height is the average height of the polygon nodes. To adjust the position of the plane, change the position of the MultiScatter.
- Exclude: List of MultiScatterExcludes which apply to the parent MultiScatterItem. If left empty, automatically all MultiScatterExclude attached to the MultiScatter apply.
- Density Map: Assign a black&white image as density map for instance distribution. White = 100% distribution, Black = 0% distribution. If left empty it uses 100% distribution for the whole area. Scale, rotate and position the PMFlat instance in order to position the density map. The density map is only shown in the editor mode, not when the game is running. To remove the density from the editor view, hide it in the editor. Note: Optionally: Instead of an exclude area, a density map with black areas can be used as well.
- Random scale type: Selects the type random scale for the spawned objects
- None: Random scale is deactivated
- Proportional: Uses proportional random scale. - Unproportional: Uses unproportional scale.
- Proportional random scale: The object to be spawned is scaled proportionally with the same value on each axis so that the object's proportion remain intact.
- Max Random scale: The maximum scale factor.
- Min Random scale: The minimum scale factor. - Scale curve: Set up a curve to adjust the scale factor distribution.
- Unproportional random scale: The object to be spawned is scaled proportionally with different scale factors for each axis. This doesn't keep the object's proportion.
- Max unproportional scale: The maximum scale factor for each axis.
- Min unproportional scale: The minimum scale factor for each axis.
- Rotation:
- Randomize Rotation: Enable random rotation for the spawned instances.
- Max random rotation: Set up the maximum angle for each rotation axis. - Min random rotation: Set up the minum angle for each rotation axis.
PMFloating
PMFloating - PlacementMode Floating - distributes the MultiMeshInstances floating in space. To adjust the position of the base plane, change the position of the MultiScatter.
- Min Max Height: the minimum and maximum height calculated from the average height of the polygon's average height.
- Exclude: List of MultiScatterExcludes which apply to the parent MultiScatterItem. If left empty, automatically all MultiScatterExclude attached to the MultiScatter apply.
- Density Map: Assign a black&white image as density map for instance distribution. White = 100% distribution, Black = 0% distribution. If left empty it uses 100% distribution for the whole area. Scale, rotate and position the PMFloating instance in order to position the density map. The density map is only shown in the editor mode, not when the game is running. To remove the density from the editor view, hide it in the editor. Note: Optionally: Instead of an exclude area, a density map with black areas can be used as well.
- Random scale type: Selects the type random scale for the spawned objects
- None: Random scale is deactivated
- Proportional: Uses proportional random scale. - Unproportional: Uses unproportional scale.
- Proportional random scale: The object to be spawned is scaled proportionally with the same value on each axis so that the object's proportion remain intact.
- Max Random scale: The maximum scale factor.
- Min Random scale: The minimum scale factor. - Scale curve: Set up a curve to adjust the scale factor distribution.
- Unproportional random scale: The object to be spawned is scaled proportionally with different scale factors for each axis. This doesn't keep the object's proportion.
- Max unproportional scale: The maximum scale factor for each axis.
- Min unproportional scale: The minimum scale factor for each axis.
- Rotation:
- Randomize Rotation: Enable random rotation for the spawned instances.
- Max random rotation: Set up the maximum angle for each rotation axis. - Min random rotation: Set up the minum angle for each rotation axis.
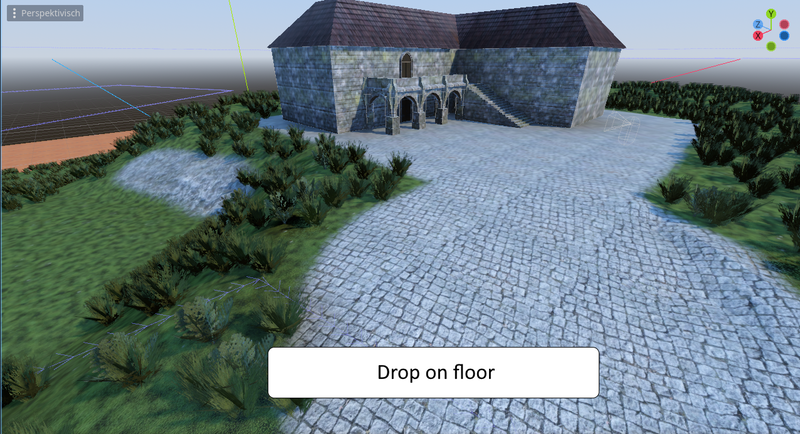
PMDropOnCollider
PMDropOnCollider - PlacementMode drop on collider - distributes the MultiMeshInstances dropped onto an object with a collision shape. First (like PMFlat) the MuliMesh position is the plane set up by the MultiScatter polygon. Then a raycast into the specified direction (up or down) takes place to determine the position on the y-axis. Once the raycast hits an object identified by it's collision mask, it places the object at that position.
Therefore: For direction "Down", the MultiScatter polygon area mus be located above the collision object. For the direction "Up", the MultiScatter polygon must be located underneath the collision object.
Collision Mask: specifies the collision mask onto which the MultiMesh instances shall be dropped.
Placement Direction: From the MultiScatter's polygon plane: Up or down.
Normal Influence: Set up how strong the surface orientation of the collision object affects the orientation of the spawned MultiMesh instance. 0 = no influence at all, 1 = exact orientation of the surface.
Exclude: List of MultiScatterExcludes which apply to the parent MultiScatterItem. If left empty, automatically all MultiScatterExclude attached to the MultiScatter apply.
Density Map: Assign a black&white image as density map for instance distribution. White = 100% distribution, Black = 0% distribution. If left empty it uses 100% distribution for the whole area. Scale, rotate and position the PMDropOnCollider instance in order to position the density map. The density map is only shown in the editor mode, not when the game is running. To remove the density from the editor view, hide it in the editor. Note: The density map for the PMDropOnCollider node is projected onto the collision objects (Decal). So it must be large enough to be visible.
Note Optionally: Instead of an exclude area, a density map with black areas can be used as well.
Random scale type: Selects the type random scale for the spawned objects
- None: Random scale is deactivated
- Proportional: Uses proportional random scale. - Unproportional: Uses unproportional scale.
Proportional random scale: The object to be spawned is scaled proportionally with the same value on each axis so that the object's proportion remain intact.
- Max Random scale: The maximum scale factor.
- Min Random scale: The minimum scale factor. - Scale curve: Set up a curve to adjust the scale factor distribution.
Unproportional random scale: The object to be spawned is scaled proportionally with different scale factors for each axis. This doesn't keep the object's proportion.
- Max unproportional scale: The maximum scale factor for each axis.
- Min unproportional scale: The minimum scale factor for each axis.
Rotation:
- Randomize Rotation: Enable random rotation for the spawned instances.
- Max random rotation: Set up the maximum angle for each rotation axis. - Min random rotation: Set up the minum angle for each rotation axis.
PMPolygon
PMPolygon - PlacementMode polygon - distributes the MultiMeshInstances all along the MultiScatter's polygon.
- Random steps: Enable or disable random steps when positioning the MultiMesh instances at the polygon.
- enabled: The distance between the MultiMesh instances at the polygon are random.
- disabled: All MultiMesh instances have the same distance to the next instance. The length of the steps between the instances depends on the amount of items to be placed onto the polygon.
- Thickness: Sets up a maximum random offset of the MultiMesh instance sideways.
- Exclude: List of MultiScatterExcludes which apply to the parent MultiScatterItem. If left empty, automatically all MultiScatterExclude attached to the MultiScatter apply.
- Random scale type: Selects the type random scale for the spawned objects
- None: Random scale is deactivated
- Proportional: Uses proportional random scale. - Unproportional: Uses unproportional scale.
- Proportional random scale: The object to be spawned is scaled proportionally with the same value on each axis so that the object's proportion remain intact.
- Max Random scale: The maximum scale factor.
- Min Random scale: The minimum scale factor. - Scale curve: Set up a curve to adjust the scale factor distribution.
- Unproportional random scale: The object to be spawned is scaled proportionally with different scale factors for each axis. This doesn't keep the object's proportion.
- Max unproportional scale: The maximum scale factor for each axis.
- Min unproportional scale: The minimum scale factor for each axis.
- Rotation:
- Randomize Rotation: Enable random rotation for the spawned instances.
- Max random rotation: Set up the maximum angle for each rotation axis. - Min random rotation: Set up the minum angle for each rotation axis.
PMPolygonOnCollider
PMPolygonOnCollider - PlacementMode polygon - distributes the MultiMeshInstances all along the MultiScatter's polygon and drops them onto an object with a collision object. First (like PMPolygon) the MuliMesh position is the MultiScatter's polygon. Then a raycast into the specified direction (up or down) takes place to determine the position on the y-axis. Once the raycast hits an object identified by it's collision mask, it places the object at that position.
- Collision Mask: specifies the collision mask onto which the MultiMesh instances shall be dropped.
- Random steps: Enable or disable random steps when positioning the MultiMesh instances at the polygon.
- enabled: The distance between the MultiMesh instances at the polygon are random.
- disabled: All MultiMesh instances have the same distance to the next instance. The length of the steps between the instances depends on the amount of items to be placed onto the polygon.
- Thickness: Sets up a maximum random offset of the MultiMesh instance sideways.
- Exclude: List of MultiScatterExcludes which apply to the parent MultiScatterItem. If left empty, automatically all MultiScatterExclude attached to the MultiScatter apply.
- Random scale type: Selects the type random scale for the spawned objects
- None: Random scale is deactivated
- Proportional: Uses proportional random scale. - Unproportional: Uses unproportional scale.
- Proportional random scale: The object to be spawned is scaled proportionally with the same value on each axis so that the object's proportion remain intact.
- Max Random scale: The maximum scale factor.
- Min Random scale: The minimum scale factor. - Scale curve: Set up a curve to adjust the scale factor distribution.
- Unproportional random scale: The object to be spawned is scaled proportionally with different scale factors for each axis. This doesn't keep the object's proportion.
- Max unproportional scale: The maximum scale factor for each axis.
- Min unproportional scale: The minimum scale factor for each axis.
- Rotation:
- Randomize Rotation: Enable random rotation for the spawned instances.
- Max random rotation: Set up the maximum angle for each rotation axis. - Min random rotation: Set up the minum angle for each rotation axis.
MultiScatterExclude
The MultiScatterExclude defines a sub area which is left empty without any mesh generated in it. It is expected to be a child node of MultiScatter. There can be more than one MultiScatterExclude in one MultiScatter.
As done for MultiScatter: set up points of the area polygon. It only makes sense to place the polygon inside (or at least overlap) the area of the MultiScatter.
- Do not place a MultiScatterExclude completely outside the MultiScatter area (Well, if you want to: do it. But it won't have any effect then.)
- Do not cover the whole MultiScatter area with MultiScatterExclude areas. This way no meshes will be generated because there is no room for the meshes.
- MultiScatterItems can refer to specific MultiScatterExclude instances. This can be set up in the PlacementMode. Then only the selected MultiScatterExclude instances apply to that MultiScatterItem.
Generate
Once the MultiScatter set up has been completed, select the MultiScatter node again. Right next to the buttons which let you draw the polygon there is a "Generate" button. Hit the generate button and all meshes are generated and placed into your scene.
You still can edit your set up (move polygons, add/remove points to polygons, add MultiScatterItems, etc). But remember: to make these changes effective you need to hit the "Generate" button again.
Common use cases
Different types of MultiScatterItems
You can set up multiple MultiScatterItems for one MultiScatter. Each MultiScatterItem can have a different configuration (PlacementModes) which gives you a maximum control how these items will be placed into your scene. Rename the items in the scene tree to get a better overview of you scene.
Exclude areas for specific MultiScatterItems only
You have set up a complex scene with several MultiScatterItems (e.g.: grass, flowers and some trees) and you have set up multiple exclude areas (e.g.: pathways and some houses). Now you have some areas where you want to have some of the MultiScatterItems, but not all of them (e.g.: no trees between the houses, but there shall be grass).
To get this done add another MultiScatterExclude and set up the polygon for the area in which shall be excluded for some MultiScatterItems.
After that edit the placement mode of MultiScatterItems:
- If only some MultiScatterExclude areas apply for a placement mode (e.g.: the grass, which shall ignore the tree's exclude area): add an element in the exclude list and select the MultiScatterExclude which shall be effictive for this placement mode.
- If all MultiScatterExclude areas apply for a placement mode: leave it as it is. By default all MultiScatterExclude areas are applicable.
- Select the MultiScatter element and hit "generate" button again and the changes will be effective.
Collision objects
You can assign an additional scene (containing a collision object) to a MultiScatterItem. This additional scene will be placed at the same position as the MultiScatterItem. - Make sure that the size, rotation and location of the collision object matches the mesh of the MultiScatterItem. Best practice here: keep mesh and collision object at the world origin of the scene (at position 0,0,0). - Make sure that the actual number of instances of the MultiScatterItem is not too high because this will generate separated instances of the additional scene.
- Enable the "Additional Scene" feature for the MultiScatterItem
- Set up the "target node" by selecting the node of your scene tree where the additional scenes shall be dropped. Note: this should be an empty node. Do not place any relevant nodes of your scene into that node. All children of the node will be deleted when generating again.
- Drop the scene containing the collision object to the field "addintional scene"
- Select the MultiScatter element and hit "generate" button again and the changes will be effective.
- Collision objects are dropped into the scene
- Scene instances are located underneath the selected target node
Density Map
The density map gives you more control of the density of the generated instances for plane based placement modes (PMFlat, PMFloating, PMDropOnCollider). Just add a black and white image as a density map to the placement mode. For the placement modes PMFlat and PMFloating the density map is shown as a plane image in 3D space. For the PMDropOnCollider mode it is projected up- and downwards onto the objects in the scene. The image is only shown in editor mode and not when your game is running. But also it can be hidden in the editor just by hiding the placement mode.
Position, rotate and scale the placement mode so that it matches your need.
When generating the MultiMesh instances the density map defines how tight the instances are generated to each other. Areas with white colour provide a density of 100% (very tight), areas with black colour provide a density of 0% (no instance at all). Any gray colour provides a density in between. So a density map with black areas are an alternative to exclude areas.