Publisher
yihrmc
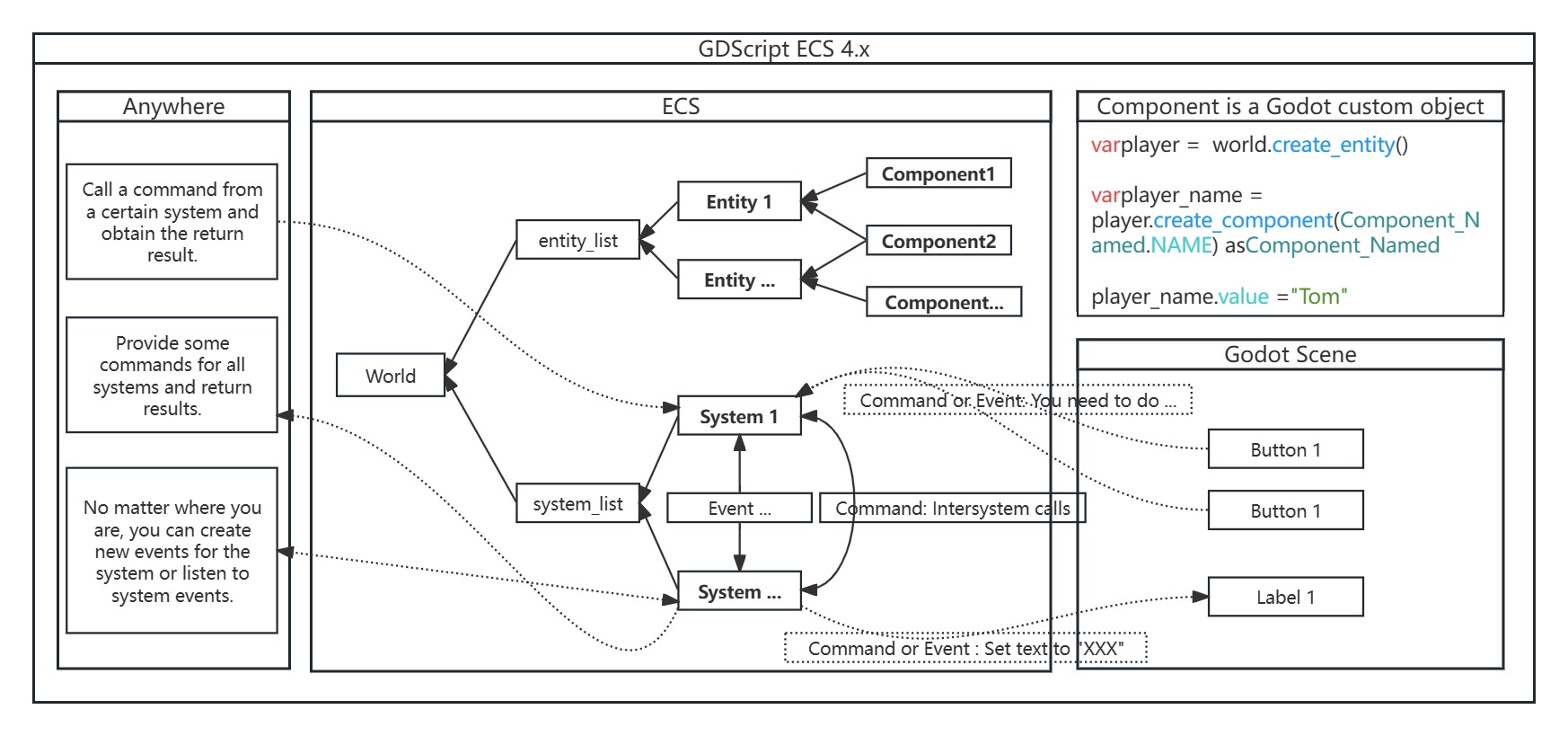
GDScript ECS 4.x
This ECS framework is very suitable for use in GDScript. Separate data and logic, get rid of the hassle of class inheritance relationships.
This plugin has been mirrored from the Godot Asset Library.
The plugin author is in no way affiliated with Gadget.
If you are the author of this plugin and would like this mirror removed, please contact support@gadgetgodot.com.
GDScript ECS framework
Warning: This ECS framework is only suitable for separating complex data computation logic.
For game rendering such as animations and related control scripts, you should use Godot's nodes.
Associate the world of ECS with your rendering nodes through the commands and events of the ECS framework.

Framework features
All ECS components support syntax prompts. Each component is a GDScript custom class.
The entity query is very fast. The entity ID is an array index.
Adding and deleting entities is still very fast. This is because the framework uses cache pooling to achieve reuse of entities.
Supports serialization, importing and exporting data without any configuration. And the data is very compact.
It is very concise and logically clear to use.
What is ECS architecture
The full name of ECS is Entity Component System. It is a software architecture primarily used for game development.
Framework concept
The framework consists of three main elements, namely 'Entity', 'Component', and 'System'. In addition, there are two elements, 'Event' and 'Command', which assist the 'System' element in completing the code logic.
Entity: It is a container for components, where an entity contains multiple components and the entity itself is not responsible for storing data.Component: Responsible for storing data. Its behavior is the same as that of a Dictionary.System: Logical processing.Event: One person can throw an event, and multiple people (or no one) can listen to the event. After throwing the event, there is no result. In fact, it is the signal in Godot.Command: One person calls the command, one person executes the command. The command allows for the return of results. In fact, it is a function.
Example
static func test():
# Add component script
var component_scanner = EcsComponentScanner.new()
component_scanner.add_script(Component_Namer)
component_scanner.add_script(Component_Test2)
# component_scanner.add_script(load("Component_xxxx.gd"))
# component_scanner.scan_script("res://gdscript_ecs_test/component/", "*.gd")
# Add system script
var system_scanner = EcsSystemScanner.new()
system_scanner.add_script(System_Test1)
system_scanner.add_script(System_Test2)
# system_scanner.add_script(load("System_xxxx1.gd"))
# system_scanner.scan_script("res://gdscript_ecs_test/system/", "*.gd")
# Initialize the world
var world := EcsWorld.new(component_scanner, system_scanner)
world.init_system() # optional
world.add_command("test_world_print", func(arg):
print("[world1_print]", arg)
pass)
# Entities created in any location
var entity = world.create_entity()
var entity_namer = entity.create_component(Component_Namer.NAME) as Component_Namer
entity_namer.display_name = "Entities created in any location"
# Processing data
for i in 15:
world.update({
count = i + 1
})
# Export world data for saving data.
var world_data = world.export_dict()
var world_data_json_str = JSON.stringify(world_data, "\t")
print("[world_data] ", world_data_json_str)
# Import data.
var world2 := EcsWorld.new(component_scanner, system_scanner)
var world_data_json = JSON.parse_string(world_data_json_str)
world2.import_dict(world_data_json)
print("[world_data2] ", JSON.stringify(world_data_json, "\t"))
# In the world of importing data,
# be sure to have the same commands and events
#
# Do you think synchronizing like this is troublesome?
# You can use the 'EcsRegisterScanner' class to implement the function of only creating commands and events.
#
world2.add_command("test_world_print", func(arg):
print("[world2_print]", arg)
pass)
# The world has been fully restored and you can call it as you please.
world2.update({
count = 1
})
pass
## Provide named data for entities
class Component_Namer extends EcsComponentBase:
const NAME = &"Namer"
## Display Name
var display_name: String = ""
class Component_Test2 extends EcsComponentBase:
const NAME = &"Test2"
var count: int = -1
class System_Test1 extends EcsSystemBase:
signal on_entity_created()
func _on_before_ready() -> void:
add_system_event(on_entity_created)
pass
func _on_update(downlink_data: Dictionary) -> Dictionary:
if downlink_data.count == 10:
# Create entities in the system
var entity = world.create_entity()
var namer = entity.create_component(Component_Namer.NAME) as Component_Namer
namer.display_name = "Test1 Entity - " + str(downlink_data.count)
var component2 = entity.create_component(Component_Test2.NAME) as Component_Test2
component2.count = downlink_data.count
downlink_data.count = 11111111111111
on_entity_created.emit()
pass
return downlink_data
pass
class System_Test2 extends EcsSystemBase:
func _on_ready() -> void:
get_event("on_entity_created").connect(__on_entity_created)
pass
func __on_entity_created():
print("[System_Test2] __on_entity_created")
pass
func _on_update(downlink_data: Dictionary) -> Dictionary:
var text = "[System_Test2] downlink_data.count: " + str(downlink_data.count)
get_command("test_world_print").call(text)
return downlink_data
pass
gdscript_ecs_test
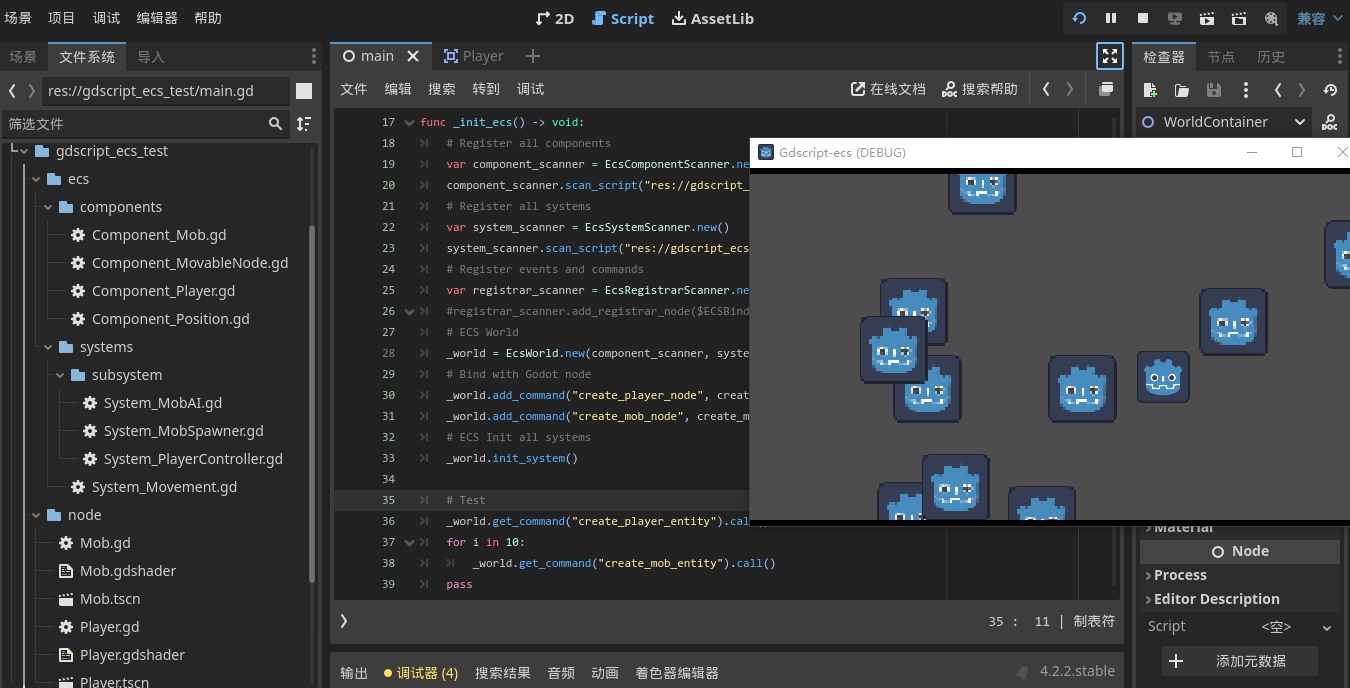
Attached is an example of the node association between ECS and Godot. In this example, the logic is all in the ECS system, please refer to the example source code directory: gdscript_ecs_test.
The demo code is still being improved, for example, archive loading has not been implemented yet.
Zip Download Notes
Due to the addition of the .gitattributes file, when downloading using zip on GitHub, the Godot project configuration file will not be included to avoid overwriting your code.
If you need the complete project configuration file for Godot, you can pull the complete code through git. With the project.godot file, you can directly use Godot to open this project without creating a new one.