Publisher
wcdev
Versatile Mobile Joystick
A highly customizable and ready-to-use joystick for mobile games in Godot. Features dynamic/fixed positioning, adjustable dead zones, and adjustable input handling. Perfect for adding responsive touch controls to your game with minimal setup.
This plugin has been mirrored from the Godot Asset Library.
The plugin author is in no way affiliated with Gadget.
If you are the author of this plugin and would like this mirror removed, please contact support@gadgetgodot.com.
Versatile Mobile Joystick for Godot
A highly customizable and easy-to-use virtual joystick plugin for Godot, perfect for mobile game development.
Features
- Simple to implement: Easy integration into your Godot project.
- Extremely customizable: Adjust every aspect of the joystick to fit your game's needs.
- Supports both fixed and dynamic positioning: Choose how the joystick appears on screen.
- Adjustable visibility modes: Control when the joystick is visible.
- Customizable input zones and responsiveness: Fine-tune the joystick's behavior to enhance gameplay.
Preview

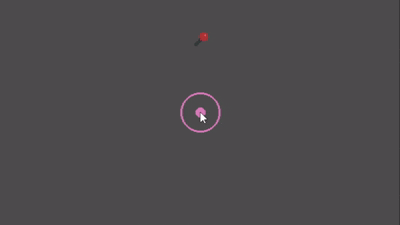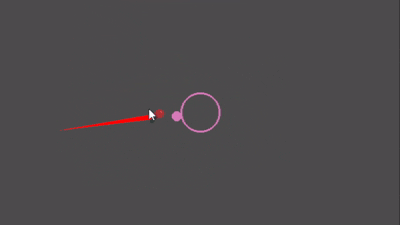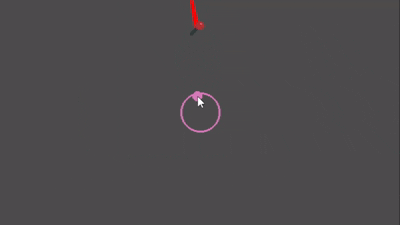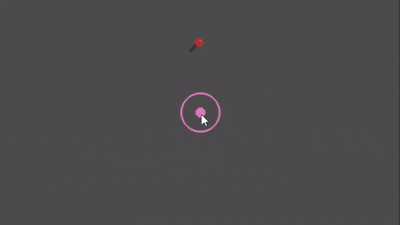
Quick Start
- Download the plugin from the AssetLib.
- Search for joystick.tscn.
- Drag and drop on any scene you want.
- Customize the joystick properties in the Inspector panel.
- Alternatively, download the addons folder and add it to your project.
Configuration Options
Here are some of the key properties you can configure:
| Category | Property | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Textures | base_texture |
The stationary part of the joystick. |
tip_texture |
The movable part that follows touch input. | |
| Behavior | joystick_mode |
FIXED (stationary) or DYNAMIC (appears at touch location). |
visibility_mode |
ALWAYS visible or WHEN_TOUCHED. |
|
| Input Zones | deadzone_circle |
Central area where input is ignored. |
tip_limit_circle |
Maximum range of joystick movement. | |
touch_detection_region |
Area where touch input is detected. | |
| Response | strength_curve |
Customize input strength translation. |
| Mapping | left_movement |
Action name for leftward movement. |
right_movement |
Action name for rightward movement. | |
up_movement |
Action name for upward movement. | |
down_movement |
Action name for downward movement. |
Recommended Project Settings
For optimal functionality, adjust the following settings in your Godot project:
- "Emulate Touch from Mouse": ON
- "Emulate Mouse from Touch": OFF
These settings ensure proper touch input handling, especially when testing on desktop environments.
Usage Tips
- Add the joystick as a child of a CanvasLayer for proper rendering on top of other elements.
- Experiment with different strength_curve settings to find the right feel for your game.
- Use the DYNAMIC joystick_mode for more flexible controls in different game scenarios.
- Adjust the deadzone_circle to prevent unintended small movements.
- Customize the touch_detection_region to create larger or smaller interactive areas.
Example Code
Here's a simple example of how to read input from the joystick in your game logic:
func _process(delta: float) -> void:
direction = Input.get_vector("ui_left", "ui_right", "ui_up", "ui_down", 0)
position += direction * speed * delta
How to Contribute
We encourage contributions from the community! If you have ideas, bug fixes, or enhancements, please:
Submit issues to report bugs or suggest features on our GitHub repository.
Create pull requests with your code changes. We appreciate:
- Clear commit messages explaining your changes.
- Tests to ensure your code works as intended.
- Documentation updates if your changes impact existing documentation.
Licensing Information
This project is released under the MIT License. For detailed license terms, please review the LICENSE file included in the repository.
Inspired by MarcoFazioRandom own Joystick